Not So Hidden Causes of Arthritis
The medical system classifies the two main forms of arthritis as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis characterized by inflammation and degeneration of one or more joints, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Arthritis encompasses over 100 other different conditions that affect joints and surrounding tissues.
From a bioenergetic perspective, if you have any form of arthritis it is because your joint is degenerating faster than you are regenerating it. In today’s article we’ll look at the true root causes as well as a more developed frame to view this pathology.
TLDR:
Conventional medicine only recognizes a partial list of causal contributors to arthritis - “wear and tear” and prostaglandins that initiate pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Linoleic Acid, the omega 6 PUFA from seed oils and LPS from gut dysbiosis are the hidden root causes that stimulate prostaglandin production.
Removing these and blocking the COX-2 enzyme responsible for creating prostaglandins eliminates the underlying conditions for arthritis to occur.
Estrogen dominance contributes to joint degeneration by up-regulating COX enzymes, whereas progesterone protects against it.
You’ll need to provide your body with the necessary energy (ATP) and raw materials to regenerate collagen. The main foods are bone broth (aminos), orange juice (vitamin c), beef liver (copper) and oysters (zinc).
Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are the two main forms of arthritis. OA is often said to be caused by mechanical "wear and tear" of cartilage due to aging, injury, or obesity.
RA is said to be an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks synovial membranes, leading to the same kind of inflammation and joint damage as OA. In both cases, the breakdown to the synovial membranes leads to cartilage breakdown. That causes bone-on-bone friction that in turn stimulates greater inflammation and degeneration. This progresses into immobility, pain, swelling, and stiffness.
The synovial membrane contains collagen types III, IV, V, and VI in its intimal layer. Type IV collagen is a key component of the synovial basement membrane, providing structural support. For reference, collagen is the most abundant protein in the the human body comprising about 30% of the total.
The synovium has three core roles: lubrication, immune surveillance and regeneration. Lubricin and hyaluronic acid are the main lubricants of the joint and the primary protectant against cartilage wear. Specialized macrophages (immune cells) form a barrier (CX3CR1+TREM2+ cells) to filter inflammatory triggers like cartilage debris, uric acid crystals, oxalates and LPS. Damage to the synovium produces inflammatory compounds (PGE₂, IL-6) that degrade cartilage. The synovial fibroblasts and macrophages coordinate repair via resolvins, growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6), and anti-inflammatory cytokines.
The center of the arthritis story revolves around the function or dysfunction of synovial membrane. Right here is where the conventional inquiry into the root cause stops. Patented medications (products) are introduced to inhibit the continued dysfunction like COX-2 inhibitors, EP4 Antagonists and if that doesn’t completely halt the destruction, your next step is a knee or hip replacement.
Wear and tear is part of the equation, but certainly not the whole of it. As I laid out in Your Stress Tolerance Threshold article, stress is personal to your current load, your history, your parents history balanced against your current ability to produce energy. The paradigm is the same here where if your use of a joint exceeds its capacity to regenerate, you will end up with arthritis.
Synovial membrane dysfunction sits at the nexus of metabolic, inflammatory, and mechanical stressors.
Poor metabolic health lowers your capacity to regenerate. Mitochondrial dysfunction leading to lowered ATP production impairs synovial fibroblast repair and macrophage phagocytosis. The reductive stress caused by the culprits responsible for electron transport chain blockages - micronutrient deficiencies, heavy metals, xenoestrogens, elevated cortisol and estrogen, omega 6 pufas - affects all tissues that have mitochondria. This includes the synovial fibroblasts. Reductive stress is the most common cause of poor ATP production. And without ATP, you cannot regenerate the joint capsule or any tissue in the body.
Chronic stress (either physical or emotional) activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, elevating cortisol. Cortisol suppresses gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), reducing luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This inhibits ovarian/testicular progesterone synthesis and progesterone levels drop, while cortisol remains elevated. Chronic cortisol depletes progesterone, exacerbating synovial inflammation. With progesterone low, estrogen becomes dominant which upregulates COX-2 and MMPs, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
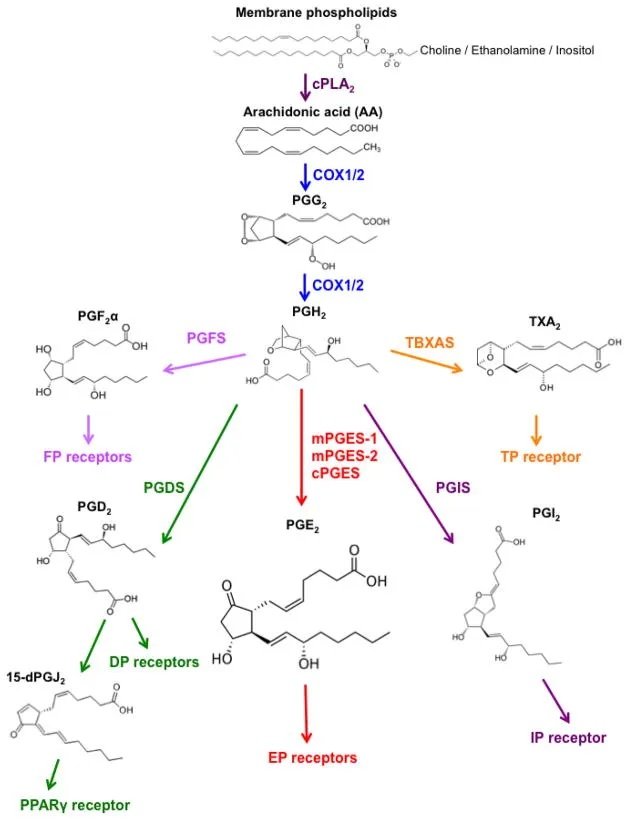
Increasing energy production means also lowering inflammatory compounds. Prostaglandin E₂ (PGE₂) and prostacyclin (PGI₂) are central mediators of synovial inflammation and cartilage breakdown in arthritis. Their roles are distinct yet interconnected, driving disease progression through shared and unique pathways.
In cartilage catabolism, PGE₂ inhibits proteoglycan synthesis (aggrecan) and stimulates MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5, enzymes that degrade collagen and aggrecan in OA cartilage. In RA, PGE₂ promotes synovial hyperplasia and osteoclast activation via EP4 receptors, accelerating bone erosion.
PGI₂ amplifies IL-6 (pro-inflammatory cytokine) production in synovial cells and enhances pain signaling. PGI₂ also synergizes with PGE₂ to drive systemic inflammation and neutrophil recruitment.
The COX enzymes, specifically COX-2, are responsible for making both PGE₂ and PGI₂.
Know what the substrate is for making PGE2? Linoleic acid (LA) omega 6 PUFAs in seed oils!
LA is converted to arachidonic acid (AA) then converted by COX-2 into PGE₂ and PGI₂.
Leaky gut and microbiome dysbiosis (LPS) directly and indirectly stimulate synovial degeneration.
In OA, LPS can pass through the intestinal barrier if you have a leaky gut and activate macrophages in the synovial lining. LPS is known to bind to the TLR4 receptor complex, which includes CD14 and MD-2. This interaction triggers a cascade of signaling pathways that lead to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6.
TLR4 also activates the COX-2 enzyme, which we previously learned turns seed oils into prostaglandins.
Since the synovial membrane and joint capsule are primarily made from collagen, it’s important to prioritize collagen production. Of course you need energy which we already covered, but you also need the raw materials.
The substrates for collagen production in the synovial capsule primarily involve amino acids glycine, proline, hydroxyproline and lysine which are essential for the triple helix structure of collagen. The simplest amino acid, glycine is crucial as it fits into the central position of the collagen triple helix due to its small size. Proline and Hydroxyproline provide stability to the collagen helix structure. Lysine is also important for cross-linking collagen fibers.
Vitamin C is a major cofactor for the prolyl hydroxylase and lysyl hydroxylase enzymes responsible for adding hydroxyl groups (-OH) to proline and lysine residues in procollagen, the precursor to collagen. This hydroxylation is crucial for the formation of the collagen triple helix structure and its subsequent cross-linking. Vitamin C also helps maintain the iron in these enzymes in its reduced state (Fe2+), which is necessary for the hydroxylation process.
Side bar…a deficiency in vitamin C leads to scurvy, characterized by weakened connective tissues, loose gums, and poor wound healing. This is due to the impaired hydroxylation of proline and lysine, resulting in defective collagen synthesis.
The minerals zinc and copper are cofactors in collagen enzymes as well. Specifically, zinc is a cofactor in collagenase, involved in collagen remodeling and repair processes. And copper is a cofactor for the lysyl hydroxylase enzyme.
Lastly, adequate protein intake is necessary to provide the building blocks for collagen production. I previously demonstrated .82g/lb as the daily target in a bioenergetic diet.
You can cover these essential materials through the consumption of bone broth or collagen powder (for the aminos), food-based vitamin c like orange juice, mango, strawberries, kiwis, red and yellow bell peppers; oysters for zinc; and beef liver for copper.
Last week I wrote about the negative implications of COX-2 produced prostaglandins have on the upregulation of the aromatase enzyme. In the context of synovial health, we can see how detrimental it can be as well.
The entire category of pain medications known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDS) specifically target the COX enzymes. These include aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Acetaminophen (Tylenol), not categorized as a NSAID, has weak COX inhibition. Avoid acetaminophen like the plague as it potently depletes your glutathione stores and can cause liver damage.
Of the three NSAIDS listed, aspirin was the first to be invented and is very safe. It has many beneficial properties of blocking COX-2 beyond dampening joint pain like improving glucose metabolism, protecting against seed oil conversion to PGE2 and inhibiting the aromatase enzyme.
Other natural COX-2 inhibitors include ginger (gingerol and shogaol), green tea (EGCG), and capers (quercetin).
Putting it all together
Optimize energy production using the bioenergetic diet and improving thyroid function.
Eliminate seed oils and replace with coconut oil, ghee/butter and tallow. Check all your packaged food and snack ingredients, you will be surprised how seed oils are everywhere.
Women, potentially supplementing progesterone.
Provide the raw material for producing collagen like bone broth, orange juice, beef liver, and oysters.
Consume COX-2 inhibitors like ginger, aspirin, green tea and capers.
Supplement Vitamin E (aromatase inhibitor).
To your health,
Jonathan
This is for informational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult with your physician or other health care professional if you have any concerns or questions about your health.